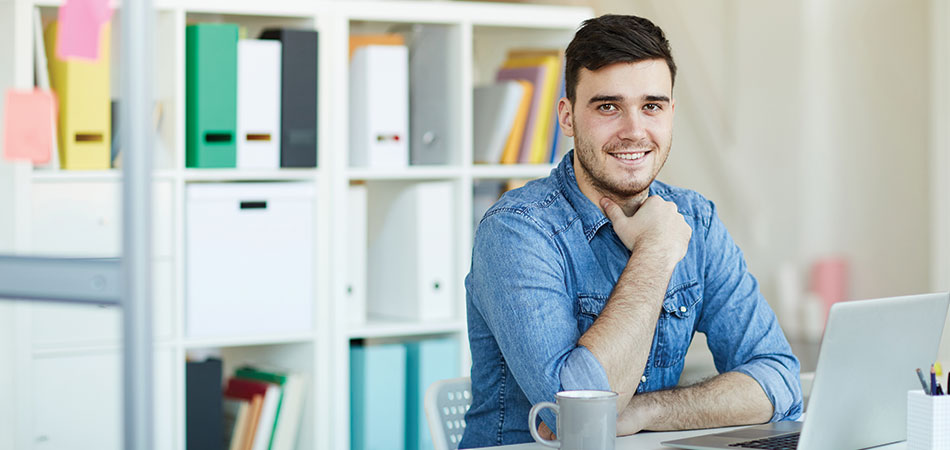
The IT industry stands at the forefront of innovation. It shapes the way we live and work. With a projected global IT market growth rate of 8.2% from 2022 to 2032, the industry offers unprecedented IT career opportunities for those who understand its breadth and potential. Let’s look at what you need to know before studying IT.
The Realm of IT: Understanding Information Technology
Information Technology specialists use technology to manage and process information. The scope of IT in 2023 extends to cutting-edge fields like AI, IoT, and cybersecurity. IT underpins everything from data management to strategic decision-making in businesses today.
IT vs. Computer Science
IT focuses on the application of technology in a business context, while computer science delves into developing new technologies and understanding computational theories. This distinction is vital for students to align their studies with their career goals.
Navigating IT Specialisations | Disciplines within IT
There’s a variety of IT career specialisation options. Some of the most common information technology roles include:
- Help Desk Technician: The first line of IT technical support, crucial for maintaining day-to-day operations.
- Systems Analyst: These professionals optimise and implement technology solutions to enhance business efficiency.
- IT Security Specialist: With the rise of cyber threats, their role in safeguarding information is more important than ever.
- Network Administrator: Responsible for maintaining the backbone of an organisation’s IT infrastructure.
- Database Administrator: They manage large volumes of data, a vital asset in today's data-driven world.
Each role demands specific skills and contributes uniquely to the IT ecosystem.
Necessary Skills and Characteristics for IT Professionals
Key skills for IT professionals include problem-solving, adaptability, and technical proficiency. Personal traits such as effective communication and teamwork are equally important, especially in collaborative IT environments.
The convergence of technical know-how, soft skills, and a growth-oriented mindset forms the backbone of a thriving IT professional.
1. Technical Proficiency: A Cornerstone Skill
A solid understanding of basic IT principles and technologies is fundamental. This includes knowledge of operating systems, networking, and database management.
Depending on your chosen IT discipline, specialised skills such as programming languages, cybersecurity measures, or cloud computing platforms become critical.
Technology is a field characterised by rapid change; you must be willing and able to learn new software, tools, and methodologies are crucial to stay relevant.
2. Problem-Solving: The Heart of IT
The ability to dissect complex problems and identify effective solutions is helpful in this field. IT specialists use a mix of creative and logical thinking; they often have to think outside the box to find solutions that are efficient and cost-effective.
IT work often involves dealing with unexpected issues and technical glitches. The ability to quickly diagnose and resolve these issues is vital.
3. Soft Skills: Bridging the Human-Technology Gap
Effective communication is needed in every job, but even more so in IT careers. You will be expected to explain technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders or collaborating with a team, clear and concise communication is essential.
IT projects often require coordinated efforts across different departments and teams. Being a team player and working effectively with others is crucial.
In roles like Help Desk Technician, a customer-focused approach is especially important. Your IT career will require empathy, patience, and the ability to understand and address user needs.
4. Business Acumen: Aligning IT with Business Goals
Knowing how businesses operate, including business strategy and objectives, enables IT professionals to better align your work with organisational goals.
Being able to manage projects efficiently, meet deadlines, and stay within budget is valuable, especially within roles like IT Project Managers or Systems Analysts.
5. Personal Attributes: The Inner Strengths of an IT Professional
Commitment to ongoing personal and professional development involves staying current with industry trends, attending workshops, and possibly pursuing advanced certifications. This will help you to stay current in your role and future proof your career in IT.
You also have to be able to handle high-pressure situations and bounce back from challenges in a field where technology emergencies usually arise unexpectedly.
Educational Pathways in IT | Preparing for an IT Education
When selecting IT courses to study, consider the content, specialisation, and study level. CompTIA A+ certification provides a foundation in IT essentials, while a CCNA certification focuses on networking skills. The value of basic IT literacy can’t be overstated.
The UK offers diverse options to study IT, from vocational courses to advanced degrees. Courses typically cover a blend of theoretical and practical aspects, preparing students for the multifaceted IT industry.
A Future-Proof Career in IT Demands Continuous Learning
The IT field is characterised by rapid technological advancements. Invest in continuous learning and stay updated with current trends such as AI and machine learning to future-proof your career.
Career Opportunities in IT | A World of Opportunities
IT skills open doors to various industries, from healthcare to finance. The diversity of IT skills reflects the same about career opportunities that are plentiful. IT skills unlock a world of career opportunities across a spectrum of industries. IT expertise is in growing demand and universal; it can transcend traditional boundaries and open doors in sectors as varied as healthcare, finance, education, and beyond. Here are some examples:
In the Healthcare Industry, an IT career could be—
As a Health Informatics Specialist, you can leverage IT to improve patient care by managing and analysing health data. A Clinical Systems Analyst implements and maintains IT solutions in clinical settings to streamline operations and enhance patient services.
IT careers in Finance and Banking include—
Fintech Developers create innovative financial technology solutions, including mobile banking apps and secure online transaction systems. IT Risk Analysts safeguard sensitive financial data against cyber threats and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Education Sector IT careers include—
Educational Technology Specialists integrate IT into educational environments to enhance learning experiences through e-learning platforms and digital classrooms.
IT Support for Educational Institutions ensure the smooth operation of IT infrastructure in schools and universities.
Government and Public Services also use IT specialist in roles such as—
Cybersecurity Analysts in Government Agencies protect critical national infrastructure and sensitive data from cyber threats. Public Sector IT Consultants advise on and implement technology solutions to improve public services and governmental processes.
Technology and Software Firms offer prestigious careers such as—
Software Developers who design, code, and test software across various platforms.
Cloud Solutions Architects develop and manage cloud computing strategies for storage and services.
If you want to work in Retail and E-Commerce IT, you could become a—
E-commerce Systems Developer: Building and optimizing online retail platforms.IT Product Managers oversee the development and deployment of tech products in the retail sector.
Entertainment and Media IT careers include—
Digital Media Specialists, who manage digital content and platforms for media companies. Game Developers creating and programming interactive gaming experiences.
These examples illustrate just a fraction of the roles available to IT professionals. The field's inherent flexibility means that IT skills are not just in demand; they are essential in nearly every industry today. This variety ensures that IT professionals can find a niche that aligns with both their skills and personal interests, making IT one of the most diverse and opportunity-rich fields.
Getting Started in IT | Embarking on Your IT Journey
Starting a career in Information Technology (IT) is an exciting and potentially rewarding decision. With the IT industry's growth projected to continue robustly into 2032 and beyond, now is an opportune time to step into this dynamic field.
Here are key steps and considerations to guide you on your journey to studying IT.
1. Identify Your IT Career Goals
Start by defining what you want to achieve in your IT career. Are you drawn to the creative aspects of web development, the problem-solving nature of cybersecurity, or the innovative realms of AI and machine learning? Understanding the wide array of career and job opportunities in IT, from network administration to database management, can help you align your educational pursuits with your career aspirations.
Everything in Agile revolves on the product. This means that product prototypes are released as soon as feasible in order to get feedback. Communication with stakeholders takes precedence over documentation or adhering to a rigorous structure.
2. Research IT Educational Pathways
The next step is to explore educational pathways that align with your goals:
- Degree Programs: Universities and colleges in the UK offer a range of IT-related degree programs. For instance, a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science focuses more on the theoretical and developmental aspects of computing, whereas a degree in Information Technology is more aligned with applying computing technologies in business contexts. Consider institutions like the University of Manchester or Imperial College London, known for their strong IT and computer science programs.
- Vocational Training and Technical Courses: Not all IT roles require a university degree. Vocational courses, often available at community colleges or through online platforms like Coursera or Udemy, offer practical, skill-focused training. For example, courses in network setup, basic programming, or IT support can be excellent starting points.
- Specialised Certifications: Certifications can enhance your employability and specialise your skill set. Key certifications include CompTIA A+ for foundational IT skills, Cisco’s CCNA for networking, CompTIA Security+ for basic security skills, and AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner for cloud computing. These certifications often require passing an exam and sometimes have recommended prerequisites like prior experience or foundational knowledge.
3. Understand the IT Market and Its Demands
Stay informed about the latest trends in the IT market. For instance, as of 2023, areas like AI, machine learning, and cybersecurity are not just buzzwords but fields experiencing substantial growth. Platforms like LinkedIn and Glassdoor can provide insights into the skills currently in demand, salary expectations, and the most sought-after IT positions.
4. Gather Resources for IT Education
There are various resources available to help you in your IT education:
- Online Learning Platforms: Websites like Coursera, edX, Career Smarter, and Khan Academy offer courses developed by reputable institutions and professionals. They are ideal for learning specific skills or gaining a broad understanding of IT concepts.
- Scholarships and Financial Aid: Investigate scholarships, grants, and bursaries offered by educational institutions, governments, and private organisations. For example, the UK government offers student loans and grants for university and college courses.
- Internships and Work Experience: Gaining practical experience is invaluable. Look for internships, part-time jobs, or volunteer opportunities in IT departments. These experiences not only provide practical skills but also help you build a professional network.
5. Develop a Learning Plan
Create a structured learning plan that outlines your educational path. This plan should include:
- A realistic timeline: Set realistic timelines for completing courses or certifications.
- Learning Objectives: Define the skills and knowledge you need to acquire at each stage of your IT education.
- Budget: Consider the costs associated with your education, including course fees, materials, and examination costs.
6. Engager with the IT Community
Join IT forums, online communities, or local tech groups. Engaging with others in the field can provide support, insights, and potential mentorship opportunities. Attend IT conferences, webinars, or workshops to stay updated with industry trends and network with professionals.
7. Build a Portfolio
As you acquire skills, start building a portfolio of your work. This could include coding projects, network setup configurations, or security solutions you have developed. A strong portfolio can be a valuable part of your resume when you start to apply for IT positions.
8. Be Flexible and Adaptable
Finally, remember that the IT field will continue to constantly evolve. Remain flexible, adaptable, and committed to lifelong learning—that is key to a successful career in IT.
A successful career in IT requires informed decision-making, a commitment to learning, and an understanding of the industry's dynamic nature. As you embark on this exciting journey, remember that the field of IT is not just about technology; it's about using technology to solve problems and create new possibilities.